Best Sleeping Positions for Rest, Recovery, and Health
After years of struggling with poor sleep and constant neck pain, I discovered something surprising: your sleeping position can have a huge impact on your health.
What started as a search for relief turned into a deep dive into the science of sleep postures. Now, I’m eager to share how the right sleeping position can not only improve your sleep but transform your overall well-being.
Let’s get into it!
The Science Behind Sleep Positions

Sleep is a complex biological process affecting every system in our body. During this time, our bodies engage in crucial restorative functions, including tissue repair, memory consolidation, and hormone regulation.
The position we sleep in significantly impacts these processes.
Certain positions affect our breathing, potentially leading to snoring or sleep apnea. Others might put unnecessary strain on our spine, resulting in back pain or poor posture over time.
Finding the right sleep position can lead to improved sleep quality, reduced pain, and better overall health.
One of the biggest challenges in optimizing sleep position is overcoming ingrained habits. Many of us have been sleeping in the same position for years, if not decades.
Changing this can feel uncomfortable at first, and it takes time for our bodies to adjust.
But with patience and persistence, the benefits can be substantial.
The Big Three: Side, Back, and Stomach Sleeping
Side Sleeping
Side sleeping is the most common sleep position, offering several health benefits.

Key Benefits of Side Sleeping:
- Reduced Snoring and Sleep Apnea: Sleeping on your side can keep your airways open, reducing the chances of snoring and sleep apnea.
- Better Spinal Alignment: With proper support, side sleeping can help maintain the natural curve of your spine.
- Improved Digestion: Lying on your left side, specifically, can assist with digestion and reduce acid reflux.
- Enhanced Brain Health: Recent studies suggest side sleeping may help the brain clear waste more efficiently, potentially lowering the risk of neurological diseases.
Tips for Better Side Sleeping:
- If you’re pregnant, consider sleeping on your left side to promote blood flow to the fetus.
- Place a pillow between your knees to align your hips.
- Select a pillow that keeps your head and neck in line with your spine.
Back Sleeping
Recommended by many orthopedic specialists, back sleeping offers a great way to maintain proper spinal alignment.
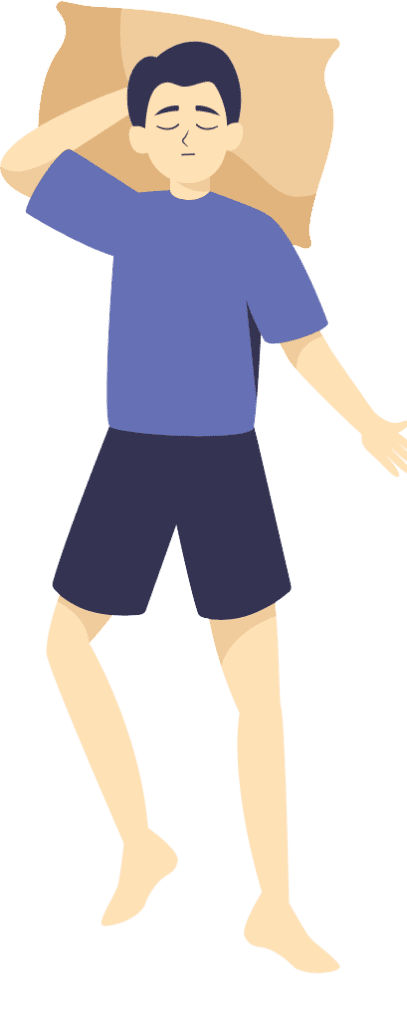

Key Benefits of Back Sleeping:
- Reduced Neck and Back Pain: This position distributes weight evenly, relieving pressure points.
- Minimized Facial Wrinkles: Without your face pressed against a pillow, you reduce the risk of developing sleep lines.
- Improved Sinus Drainage: Sleeping on your back can help mucus drain more effectively thanks to gravity.
Tips for Better Back Sleeping:
- Use a pillow that supports the natural curve of your neck.
- Consider placing a small pillow under your knees to relieve lower back pressure.
Stomach Sleeping
Although generally considered less ideal for spinal health, some people still prefer stomach sleeping.
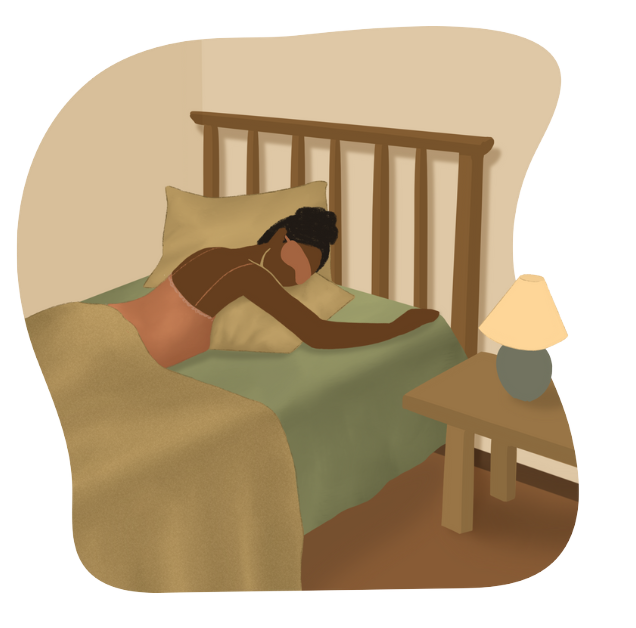

Challenges with Stomach Sleeping:
- It can strain your neck and spine, leading to pain or discomfort.
- It is not as effective for spinal alignment as side or back sleeping.
Tips for Stomach Sleepers:
- Use a thin pillow (or none at all) to minimize neck strain.
- Place a pillow under your hips to reduce pressure on your lower back.
- Consider using an extra-firm mattress to ensure proper spine alignment. Coconut husks mattresses have a extra-firm level of support that can help alleviate back pain.
- If possible, consider transitioning to side or back sleeping for better spinal health.
Related Reading: How to choose the best pillow for front sleepers
Implementing Your Optimal Sleep Position
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s walk through how to apply your optimal sleep position:
- Assess your current sleep position and any associated issues (pain, snoring, etc.).
- Choose a new position based on your needs and preferences.
- Invest in suitable pillows and supports for your chosen position.
- Start by trying your new position for short periods, like naps or the first few hours of sleep.
- Gradually increase the time spent in your new position over several weeks.
- Be patient and persistent. It can take time for your body to adjust to a new sleep position.
- Reassess after a few weeks and make adjustments as needed.
Remember, changing your sleep position is a process. It might feel uncomfortable at first, but stick with it.
The long-term benefits are worth the short-term discomfort.
Common Sleep Position Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
As you work on optimizing your sleep position, be aware of these common pitfalls:
- Expecting immediate results: It takes time for your body to adjust to a new sleep position. Give it at least a few weeks before deciding if it’s working for you.
- Ignoring pain or discomfort: While some initial discomfort is normal, persistent pain is a sign that something needs to change.
- Using the wrong pillows: The right pillow support is crucial for maintaining proper alignment in any sleep position.
- Neglecting your mattress: Even the best sleep position won’t help if your mattress isn’t supportive.
- Forcing a position that doesn’t feel natural: While certain positions have more benefits, the best position is ultimately the one that allows you to sleep comfortably and wake up feeling refreshed.
Adapting Your Sleep Position
Your optimal sleep position may change over time because of factors like age, weight, injuries, or pregnancy. Here are some tips for adapting your sleep position:
- Listen to your body: If you start experiencing new aches or pains, it might be time to reassess your sleep position.
- Experiment with variations: Small adjustments, like slightly bending your knees when back sleeping, can make a big difference.
- Use props: Pillows, bolsters, and wedges can help you maintain a comfortable position throughout the night.
- Consider your sleep environment: Factors like room temperature and bedding can affect how comfortable you are in different positions.
- Be flexible: It’s okay to switch between positions if that’s what feels best for your body.
Building on the Basics
Understanding and optimizing your sleep position is just the beginning of mastering the art of sleep. As you become more attuned to how your body responds to different sleep positions, you’ll likely notice other aspects of your sleep environment that could use improvement.
This might lead you to explore topics like sleep hygiene, circadian rhythms, or the impact of diet and exercise on sleep quality. Each of these areas offers opportunities for further sleep optimization.
Exercises to Reinforce Your New Sleep Position
To help reinforce your new sleep position, try these exercises:
- Mindful positioning: As you get into bed each night, take a moment to consciously position your body in your chosen sleep posture.
- Pillow check: Regularly assess your pillows to confirm they’re still providing adequate support.
- Morning reflection: When you wake up, take note of your position and how you feel. This can help you track progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Stretching routine: Develop a pre-bed stretching routine that targets the muscles used in your preferred sleep position.
- Daytime posture practice: Work on maintaining good posture during the day to support your nighttime alignment.
The Impact of Sleep Position on Health Conditions
Your sleep position can have a significant impact on various health conditions. Let’s explore some of these connections:
Sleep Apnea and Snoring
Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, can be significantly affected by sleep position. Back sleeping often exacerbates sleep apnea and snoring, as it allows the tongue and soft palate to collapse to the back of the throat.
Side sleeping, particularly on the left side, can help reduce these issues by keeping the airways more open.
For those with sleep apnea, positional therapy devices can help maintain side sleeping throughout the night. These devices, which can be as simple as a tennis ball sewn into the back of a sleep shirt, discourage rolling onto the back during sleep.
Acid Reflux and GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and acid reflux can be particularly troublesome at night. Left-side sleeping has been shown to reduce acid reflux symptoms.
This position keeps the junction between stomach and esophagus above the level of stomach acid.
Conversely, right-side sleeping may worsen GERD symptoms.
Elevating the head of the bed by 6-8 inches can also help manage nighttime acid reflux, regardless of sleep position. This can be achieved with bed risers or a wedge pillow.
Back Pain
For those with back pain, finding the right sleep position is crucial. While person needs may vary, many find relief with the following:
- Back sleeping with a pillow under the knees to maintain the spine’s natural curve
- Side sleeping with a pillow between the knees to keep the hips aligned
- Stomach sleeping (if necessary) with a thin pillow under the hips to reduce lower back strain
It’s important to maintain proper spinal alignment in any position. A supportive mattress and suitable pillows play a key role in this.
Pregnancy
Sleep positions become particularly important during pregnancy. As the pregnancy progresses, back sleeping can compress the inferior vena cava, potentially reducing blood flow to the fetus.
Left-side sleeping is often recommended as it can improve blood flow to the uterus.
Pregnant women may find comfort by using extra pillows:
- Between the knees to reduce hip pressure
- Under the belly for support
- Behind the back to prevent rolling onto the back during sleep
The Role of Sleep Position in Pain Management
Sleep position can play a significant role in managing various types of pain:
Neck Pain
For those with neck pain, maintaining proper alignment is crucial. Back sleeping with a supportive pillow that fills the space between the neck and mattress can help.
Side sleepers should confirm their pillow keeps their neck in line with their spine.
Avoid sleeping on your stomach if you have neck pain, as this position often leads to twisting of the neck.
Shoulder Pain
If you’re dealing with shoulder pain:
- Avoid sleeping on the affected side
- Try back sleeping with a small pillow supporting the affected arm
- If side sleeping, hug a pillow to your chest to support the upper arm
Hip Pain
For hip pain sufferers:
- Side sleeping with a pillow between the knees can help align the hips
- Back sleeping with a thin pillow under the knees can reduce pressure on the hips
- Avoid sleeping on the painful side
Sleep Position and Cognitive Health
Emerging research suggests that sleep position may influence cognitive health. A 2015 study published in the Journal of Neuroscience found that side sleeping may be more efficient at removing brain waste compared to other sleep positions.
This waste removal process, known as the glymphatic system, is thought to play a role in preventing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
While more research is needed to fully understand this connection, it provides another compelling reason to consider side sleeping.
The Influence of Culture on Sleep Position
Sleep positions can vary significantly across cultures. For example:
- In Japan, many people traditionally sleep on futons placed directly on the floor, which can influence sleep posture.
- Some cultures practice co-sleeping, where parents sleep in the same bed as their children, which can affect sleep positions for all involved.
- In some parts of Africa and South America, hammock sleeping is common, which naturally encourages a curved, somewhat fetal position.
These cultural differences remind us that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to sleep position. What works best can depend on person factors, including cultural background and personal preference.
How Your Sleep Position Affects Mattress Choice
Your sleep position should tell your mattress choice:
- Side sleepers often benefit from softer mattresses that allow the hips and shoulders to sink in slightly, maintaining spinal alignment.
- Back sleepers typically need a medium-firm mattress that supports the lower back while contouring to the body’s shape.
- Stomach sleepers usually need a firmer mattress to prevent the hips from sinking too deeply, which can strain the lower back.
When shopping for a mattress, always test it in your preferred sleep position. Many mattress companies now offer extended trial periods, allowing you to truly assess if the mattress supports your sleep position over time.
The Connection Between Sleep Position and Snoring
Snoring, while often seen as a mere nuisance, can be a sign of sleep apnea and can significantly impact sleep quality. Sleep position plays a crucial role in snoring:
- Back sleeping is the position most likely to induce snoring. In this position, the tongue and soft palate are more likely to collapse to the back of the throat, partially blocking the airway.
- Side sleeping can help reduce snoring by keeping the airways more open.
- Elevated head position can also help. Using an adjustable bed or extra pillows to slightly elevate the head can reduce snoring for some people.
If snoring persists regardless of sleep position, it’s important to ask a healthcare provider, as it may show sleep apnea or another underlying condition.
How Sleep Position Impacts Circulation: Tips for Better Blood Flow and Health
Your sleep position can affect your circulation:
- Left-side sleeping is often recommended for improved circulation. This position aids the flow of blood back to the heart.
- Elevated legs can help with circulation issues. This can be achieved by slightly elevating the foot of the bed or using pillows under the legs.
- Avoid positions that cut off circulation to limbs. For example, sleeping with an arm under your head for extended periods can lead to numbness and tingling.
Good circulation during sleep is crucial for overall health and can help prevent issues like varicose veins and edema.
The Impact of Sleep Position on Skin Health
Your sleep position can affect your skin, particularly facial skin:
- Back sleeping is often considered best for preventing facial wrinkles, as it doesn’t create pressure points on the face.
- Side and stomach sleeping can lead to “sleep wrinkles” over time due to the face being pressed against the pillow.
- Silk or satin pillowcases can help reduce friction on the skin, regardless of sleep position.
Remember, while skin health is a consideration, it shouldn’t override comfort and overall sleep quality when choosing a sleep position.
Sleep Position and Temperature Regulation
Your sleep position can influence how your body regulates temperature during the night:
- Spread-eagle position on the back allows for most air circulation around the body, which can help with cooling.
- Fetal position (tightly curled on the side) reduces the surface area exposed to air, which can help keep warmth.
- Stomach sleeping with one leg raised (sometimes called the “sprinter” position) can help regulate temperature by allowing one part of the body to be cooler than the other.
Considering temperature regulation when choosing a sleep position can be particularly helpful for those who tend to sleep hot or cold.
The Relationship Between Sleep Position and Dreams
While the content of our dreams is largely influenced by our waking experiences and subconscious mind, some research suggests that sleep position might play a role:
- A study published in the journal Dreaming found that left-side sleepers reported more nightmares, while right-side sleepers had more positive dreams.
- Some researchers hypothesize that different sleep positions might affect blood flow to the brain, potentially influencing dream content.
While this area needs more research, it’s an intriguing aspect to consider when exploring sleep positions.
Sleep Position and Aging
As we age, our optimal sleep position may change:
- Older adults often find side sleeping more comfortable due to issues like arthritis or back pain.
- The use of supportive pillows becomes increasingly important to maintain proper alignment and reduce pressure points.
- Adjustable beds can be useful for older adults, allowing for customized positioning to address specific health concerns.
It’s important to reassess your sleep position periodically as you age to confirm it still meets your changing needs.
The Role of Sleep Position in Athletic Recovery
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, sleep position can play a role in recovery:
- Side or back sleeping can help maintain proper spinal alignment, which is crucial for athletes dealing with back strain.
- Elevated leg position can help with reducing swelling and promoting circulation after intense lower body workouts.
- Some athletes find that varying their sleep position can help prevent overuse injuries from developing.
Proper sleep positioning should be considered an integral part of any athletic recovery routine.
Sleep Position and Digestion
Your sleep position can affect your digestive process:
- Left-side sleeping is often recommended for better digestion. This position allows gravity to assist the movement of waste through the colon.
- Slightly elevated head position can help with digestion and reduce symptoms of acid reflux.
- Avoid eating large meals close to bedtime, regardless of sleep position, to prevent digestive discomfort during the night.
Considering your digestive health when choosing a sleep position can lead to more comfortable and restful nights.
The Influence of Sleep Position on Breathing
Your sleep position significantly affects your breathing:
- Side sleeping, particularly left-side sleeping, can help keep airways open and reduce snoring and sleep apnea symptoms.
- Back sleeping can exacerbate breathing issues for some people, as it allows the tongue to fall back and partially obstruct the airway.
- Elevated head position can help with breathing issues by using gravity to keep airways more open.
For those with respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD, finding the right sleep position can be crucial for managing symptoms and ensuring restful sleep.
Sleep Position and Spinal Health
Maintaining proper spinal alignment during sleep is crucial for overall health:
- Back sleeping with proper support can help maintain the natural curve of the spine.
- Side sleeping with a pillow between the knees helps keep the spine aligned.
- Stomach sleeping can put strain on the lower back and neck, and should generally be avoided if you have spinal issues.
Regular chiropractic check-ups can help confirm your sleep position is supporting good spinal health.
The Connection Between Sleep Position and Hormones
Emerging research suggests that sleep position might influence hormone production:
- Some studies show that right-side sleeping might increase melatonin production, potentially improving sleep quality.
- Left-side sleeping may help with lymphatic drainage, which could influence the balance of stress hormones in the body.
While more research is needed in this area, it’s an exciting frontier in understanding the full impact of sleep position on our health.
Sleep Position and Comfort: Finding Your Perfect Match
Ultimately, the best sleep position is one that allows you to sleep comfortably and wake up feeling refreshed. Here are some final tips for finding your perfect sleep position:
- Experiment with different positions over several weeks to find what feels most natural and comfortable.
- Invest in quality pillows and mattresses that support your preferred position.
- Consider your health conditions and how different positions might affect them.
- Be open to change as your body’s needs evolve over time.
- Listen to your body – if you consistently wake up with pain or discomfort, it’s time to reassess your sleep position.
Remember, good sleep is basic to overall health and well-being. Taking the time to improve your sleep position is an investment in your long-term health and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the healthiest sleeping position?
While person needs vary, side sleeping is often considered the healthiest position for most people. It can help reduce snoring, reduce acid reflux, and may even benefit brain health.
Can sleeping position affect back pain?
Yes, sleep position significantly impacts back pain. Back sleeping with a pillow under the knees or side sleeping with a pillow between the knees can help reduce back pain for many people.
Is it bad to sleep on your stomach?
Stomach sleeping can put strain on your lower back and neck. While not recommended for most people, if you’re a committed stomach sleeper, use a thin pillow or no pillow to minimize neck strain.
How can I stop snoring by changing my sleep position?
Side sleeping, particularly on the left side, can help reduce snoring by keeping airways more open. Elevating your head slightly can also help.
What’s the best sleeping position for acid reflux?
Left-side sleeping is often recommended for acid reflux. This position keeps the junction between stomach and esophagus above the level of stomach acid.
Can sleep position affect wrinkles?
Yes, sleeping on your side or stomach can lead to “sleep wrinkles” over time due to facial compression against the pillow. Back sleeping may help prevent this.
What’s the best sleeping position during pregnancy?
Left-side sleeping is often recommended during pregnancy as it can improve blood flow to the uterus. Using supportive pillows can increase comfort.
How does sleep position affect circulation?
Left-side sleeping can aid circulation by making it easier for the heart to pump blood through the body. Elevated legs can also help with circulation issues.
Can sleep position influence dreams?
Some research suggests that sleep position might influence dream content, with left-side sleepers reporting more nightmares. However, more research is needed in this area.
How often should I change my sleep position?
There’s no set rule, but it’s a good idea to reassess your sleep position if you start experiencing new aches, pains, or sleep disturbances. As we age or if our health changes, our optimal sleep position may change too.
Key Takeaways
- Side sleeping, particularly on the left side, offers many health benefits including reduced snoring and improved digestion.
- Back sleeping can be useful for spinal alignment but may exacerbate snoring and sleep apnea.
- Stomach sleeping is generally not recommended due to potential strain on the neck and lower back.
- The right pillows and supports are crucial for maintaining proper alignment in any sleep position.
- Sleep position can significantly impact various health conditions including acid reflux, back pain, and pregnancy discomfort.