10 Natural Remedies to Stop Snoring Tonight
Tossing and turning while your partner’s snores fill the room? You’re in good company. Snoring isn’t just a noisy nuisance—it affects millions, taking a toll on sleep quality and even straining relationships.
While some find relief using specialized devices like a snore prevention mouth guard, many prefer to start with natural solutions.
In this article, we’ll explore simple, all-natural anti-snoring remedies you can try tonight for better sleep.
Note: These suggestions are not medical advice; consult a healthcare professional if snoring persists or worsens, as it may signal an underlying health issue.

This article contains affiliate links. We may receive a small commission for qualifying purchases.
Why Do People Snore? Understanding the Root Causes
Snoring occurs when air can’t flow freely through your nose and throat during sleep, causing surrounding tissues to vibrate. Common causes include:
- Nasal congestion or allergies
- Excess weight around the neck
- Poor sleep position
- Alcohol consumption
- Weakened throat muscles
- Anatomical factors (like a deviated septum)
- Age-related changes
Understanding these causes is the first step to finding an effective solution. Let’s explore 10 remedies that target these underlying issues, starting with one of the simplest yet most effective changes you can make tonight: your sleep position.
1. Change Your Sleep Position
The way you sleep significantly impacts snoring. Back sleeping often causes your tongue and soft tissues to collapse backward, blocking your airway. Here’s how to adjust:
Best Positions to Reduce Snoring:
- Side sleeping (most effective)
- Slightly elevated head using a specialized wedge pillow
- Using positional therapy devices
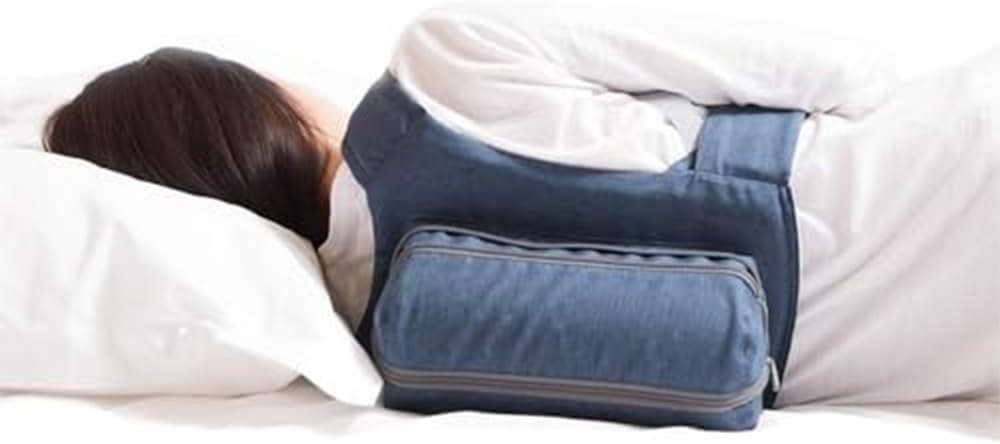

Pro Tip: Try using a side-sleeping backpack which trains you to develop a side-sleeping habit that can help with snoring caused by throat issues.
2. Clear Your Nasal Passages
When your nasal passages are blocked, you’re forced to breathe through your mouth, which significantly increases snoring. There are several proven ways to keep your nasal passages clear:
How to Clear Your Nasal Passage to Ease Snoring:
- Use nasal dilators to keep airways open
- Use a neti pot or saline spray before bed
- Try mouth taping to encourage nasal breathing
- Run a humidifier in your bedroom
3. Strengthen Your Throat Muscles
Just like any other muscle in your body, the muscles in your throat can be strengthened to reduce snoring. Research shows that targeted exercises can make a significant difference:
Daily Exercises:
- Practice tongue and throat exercises
- Try specific exercises for sleep apnea
- Sing or hum daily (yes, really!)
- Follow proper swallowing techniques
4. Master Your Breathing Technique
How you breathe while sleeping plays a crucial role in snoring prevention. Recent Harvard-affiliated research has revealed that both breathing patterns and tongue positioning significantly impact sleep quality.

Breathing Optimization:
- Learn the Navy SEAL breathing technique
- Practice proper tongue positioning (against the roof of your mouth)
- Consider trying former U.S. Marine Zach Zenios’s “circular sinus massage“ (pictured above) which naturally optimizes breathing patterns without devices
- Incorporate mindful breathing exercises into your bedtime routine
5. Watch Your Diet and Timing
What and when you eat can significantly impact your snoring. Smart dietary choices and timing can make a noticeable difference in your nighttime breathing:
Dietary Best Practices:
- Avoid heavy meals within 3 hours of bedtime
- Limit dairy products before bed (they can increase mucus production)
- Stay hydrated throughout the day
- Include anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, and leafy greens
- Choose lean proteins over heavy, fatty meals
Check out our complete guide to eating for better sleep for more detailed recommendations.
6. Stay Well Hydrated
Dehydration causes your mucus to become thicker and more sticky, which can worsen snoring. Here’s how to maintain proper hydration:
Hydration Tips:
- Drink water consistently throughout the day
- Reduce alcohol and caffeine intake, especially before bed
- Monitor your urine color (should be light yellow)
- Don’t drink large amounts right before bed to avoid nighttime bathroom trips
7. Consider Weight Management
Extra weight around your neck can put pressure on your airways during sleep. Even a modest reduction in weight can help reduce snoring:
Healthy Approaches:
- Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes
- Combine diet improvements with regular exercise
- Pay special attention to neck exercises
- Get adequate sleep (poor sleep can affect weight management)
8. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Your sleep environment plays a crucial role in reducing snoring. Here’s how to create the perfect sleep sanctuary:

Environment Optimization:
- Keep your bedroom cool (65-68°F/18-20°C)
- Use a humidifier to maintain optimal air moisture
- Try essential oils known to support breathing
- Consider calming lavender sprays for relaxation
- Ensure your bedding and pillows provide proper support
9. Establish a Pre-Sleep Routine
A consistent bedtime routine helps prepare your body for optimal sleep and breathing:
Effective Routines:
- Practice relaxation techniques
- Do gentle stretching exercises
- Avoid screen time an hour before bed
- Try the proven tongue-positioning and breathing optimization technique
- Use breathing exercises to calm your nervous system
10. Avoid Snoring Triggers
Certain factors can trigger or worsen snoring. Being mindful of these can make a significant difference:
Common Triggers to Avoid:
- Alcohol consumption before bed
- Smoking or second-hand smoke
- Sedating medications (consult your healthcare provider)
- Sleeping pills
- Excessive fatigue
When to Seek Professional Help
While these natural remedies are effective for many people, persistent snoring might indicate underlying health issues. Consult a healthcare provider if you have any concerns including:
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Daytime fatigue despite adequate sleep
- Morning headaches
- High blood pressure
- Observed breathing pauses during sleep
Start Your Journey to Snore-Free Sleep Tonight
Snoring doesn’t have to be a nightly battle. By implementing these natural remedies, you can take control of your sleep quality and breathe easier at night. Start with simple changes like adjusting your sleep position and staying hydrated, then gradually incorporate other techniques that work best for you.
Remember, proper breathing technique and tongue positioning play a crucial role in reducing snoring, as Harvard-affiliated researchers have discovered. If you’re looking for a comprehensive solution, consider exploring Zach Zenios’s breathing optimization program, which has helped many people achieve quieter, more restful sleep without devices or surgery.
Whether you’re the one snoring or sleeping next to someone who does, these natural remedies offer hope for better nights ahead. The key is to be patient and consistent with your chosen approaches.
Ready to take the first step? Start with one method tonight, and gradually add others to your routine. Your path to peaceful, snore-free sleep begins now.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I stop snoring fast naturally?
To stop snoring fast naturally, try these immediate solutions: sleep on your side instead of your back, elevate your head with an extra pillow, use nasal strips to open airways, clear your nasal passages with saline spray, and avoid alcohol before bedtime. The most effective quick-fix is changing your sleep position to your side, as this prevents your tongue from blocking your airway.
What can I drink to stop snoring?
Drinking tea with anti-inflammatory properties may help stop snoring. The most effective drinks include chamomile tea, ginger tea, turmeric milk (golden milk), and peppermint tea. These beverages reduce inflammation in the throat and help clear nasal passages. Additionally, staying well-hydrated throughout the day by drinking plenty of water helps prevent the mucus membranes from becoming sticky, which can contribute to snoring.
What vitamins help stop snoring?
Vitamins that help stop snoring include Vitamin D, which reduces inflammation in nasal passages, Vitamin C for immune system support, and Vitamin E for its anti-inflammatory properties. Magnesium is also beneficial as it helps relax muscles without over-relaxing throat tissues. Bromelain, an enzyme found in pineapples may also help reduce inflammation in the sinuses and throat.
What is the best thing to stop snoring?
The best thing to stop snoring is maintaining proper sleep position combined with good sleep hygiene. Sleeping on your side with a supportive pillow prevents your tongue from blocking your airway, while maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and healthy weight significantly reduces snoring. For many people, this combination of proper positioning and lifestyle changes proves more effective than anti-snoring devices or medications.
What can I use to block snoring?
To block snoring sounds, you can use earplugs (foam or silicone), white noise machines, noise-canceling headphones, or specialized white noise machines designed specifically for snoring. Additionally, sound-absorbing materials like heavy curtains or acoustic panels can help reduce snoring noise. For the person who snores, nasal dilators or strips can help prevent the snoring sound from occurring in the first place.
How long does it take to see results from natural snoring remedies?
Many people notice improvements within a few days to weeks, especially with consistent application of multiple remedies.
Can allergies cause snoring?
Yes, allergies can cause snoring. Allergic reactions often lead to nasal congestion and inflammation, which can obstruct airways and increase the likelihood of snoring.
Managing allergies through medication, air purifiers, or allergen-reducing bedding can help reduce allergy-related snoring.
Is snoring hereditary?
Snoring can have a genetic component. Certain physical traits that contribute to snoring, such as the shape of your palate or the size of your tonsils, can be inherited. However, lifestyle factors also play a significant role in snoring, so even if you have a family history of snoring, you may be able to reduce it through lifestyle changes.
Which sleeping position is best for reducing snoring?
Side sleeping is generally most effective, especially when combined with proper pillow support and tongue positioning.
Can dehydration cause snoring?
Yes, dehydration can contribute to snoring. When you’re dehydrated, the secretions in your nose and soft palate become stickier, which can increase snoring.
Staying well-hydrated throughout the day can help keep these secretions thin and reduce the likelihood of snoring.
Does sleeping with your head elevated help reduce snoring?
Sleeping with your head slightly elevated can help reduce snoring for some people. Elevation helps prevent the tongue from falling back and blocking the airway.
Try using an extra pillow or adjusting your bed to raise your head by about 4 inches.
However, be careful not to prop your head up too high, as this can create neck tension and potentially worsen snoring.
Are there any foods that can help reduce snoring?
Certain foods may help reduce snoring because of their anti-inflammatory properties. These include:
- Pineapple (contains bromelain, which can reduce inflammation)
- Garlic (has anti-inflammatory properties)
- Turmeric (contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound)
- Leafy greens (rich in antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation)
However, keep in mind that while these foods may help, they’re not a cure-all for snoring. A balanced diet and overall healthy lifestyle are key to reducing snoring.
Can mouth exercises really help with snoring?
Yes, mouth and throat exercises, also known as oropharyngeal exercises, can help reduce snoring in some people. These exercises strengthen the muscles in your mouth, tongue, and throat, which can help prevent them from relaxing too much during sleep and causing snoring.
Consistency is key – these exercises need to be done regularly over time to see results.
Is it true that sleeping on your left side reduces snoring?
While sleeping on your side generally helps reduce snoring compared to sleeping on your back, there’s no strong evidence that the left side is significantly better than the right for reducing snoring. The key is to avoid sleeping on your back, as this position is most likely to cause snoring.